Also Known As: Chipboard, Pressboard, Fiberboard
What are Particleboard and MDF Composite Wood Panels?
Particleboard and MDF (medium-density fiberboard) are by far the two most common substrates for decorative laminates and veneers. They are cost-effective, dimensionally stable, utilize resources that are usually close to production facilities, and can be engineered for a variety of special properties and applications.
Why Use Composite Wood Panels?
Learn more about a very important reason to use these materials in building and design at ClimatePositiveNOW.org.
For carrying decorative surfaces, there really aren’t any practical alternatives to these composite wood panels. Nothing else offers their value, flexibility, and ability to be fabricated with standard woodworking tools.
Plus, every composite wood panel essentially starts its life as a recycled material.
Production Uses Recycled Wood Fiber
Most or all of the wood fiber in particleboard and MDF is recovered from other operations – industrial wood residues (recycled pre-consumer residue) such as shavings, sawdust and plywood trim and chips, chips from logs, and urban wood waste (post-consumer residue). Panels can also be produced from agri-fiber sources.
This wood fiber would otherwise be landfilled or burned.
Locally Sourced Fiber from Managed Forests
Particleboard and MDF are widely available, and often made with locally sourced fiber from FSC-certified forests and lumber and furniture operations, minimizing transportation. Some suppliers plant and manage their own forests of fast-growing trees that mature in 25 or 30 years, versus 60-80 years. This creates a healthier environment: younger trees absorb more carbon and produce more oxygen than older trees.
Composite wood panels allow the industry to 99 percent of the tree. Originally, this approach had nothing to do with being “green.” It was just a practical approach to getting the most out of a carefully managed natural resource.
Composite Wood Panels Meet Stringent IAQ Requirements
All panels produced in North America meet or exceed CARB2 (California Air Resources Board version 2) requirements for indoor air quality.
Composite Wood Panels are an Effective Carbon Sink
- Wood stores carbon as it grows.
- 50% of wood’s chemical structure is absorbed carbon, which is not released back into the atmosphere until it burns or decomposes.
- The carbon sink properties of the wood in composite panels more than offset its carbon footprint, including manufacture and transportation.
- Their net carbon footprint, therefore, is negative, actually offsetting some of the CO2 in the atmosphere.
- The longer a wood-based decorative panel last in an application, the longer that carbon is sequestered.
Where are Particleboard and MDF Used?
APPLICATIONS
- Commercial and residential
- Casework, cabinetry, doors and drawers
- Worktops, tabletops, transaction counters
- Wall panels
- Flooring and underlayment
- Closet and storage systems
- Commercial Signage
Properties and Performance
Composite panels are highly stable, dimensionally consistent, and can be engineered for special performance properties:
- Moisture resistance
- Fire resistance
- Specific indoor air quality goals
- Density/screw-holding power
- Light weight
- Different thicknesses and dimensions
Material Makeup and Manufacturing
PARTICLEBOARD
Particleboard, as the name implies, is composed of small wood chips or particles. It is an economical, stable, and resource-efficient substrate for furniture and fixtures, cabinetry, shelving, floor and stair underlayment, countertops and door cores.
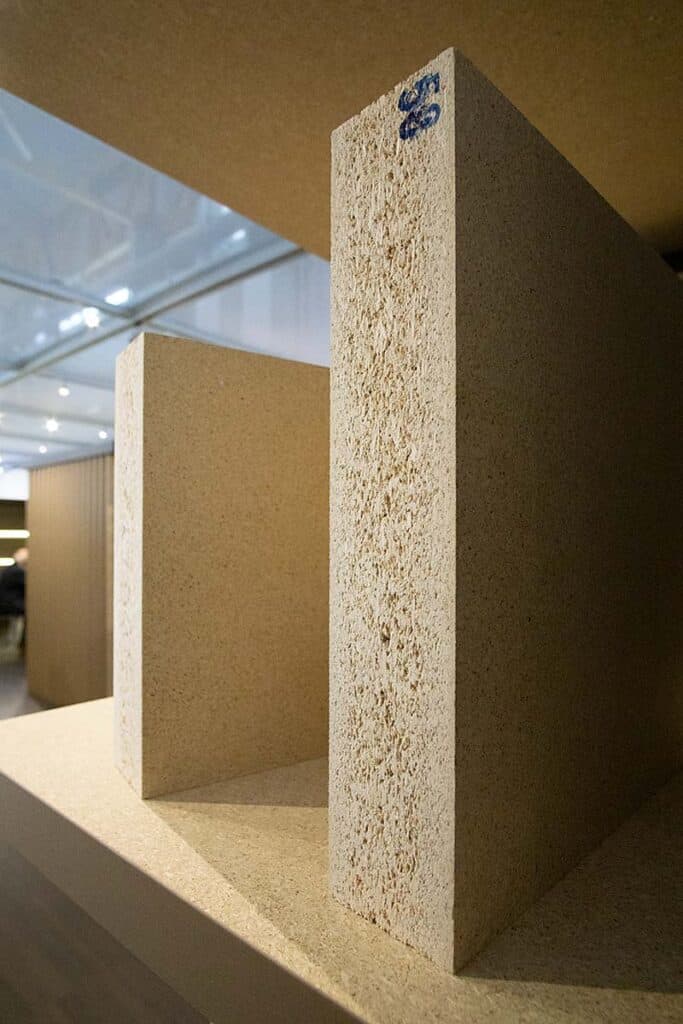

MDF
In MDF, or medium-density fiberboard, the wood is further refined down to cellulosic fibers to create a very smooth, homogenous panel that can machined with intricate detail and into complex shapes.
You’ll find MDF in:
- Furniture and fixtures
- Cabinetry
- Architectural millwork and mouldings
- Laminating and finishing
- Laminate flooring, and
- Finely detailed furniture and architectural components


Panels are produced by:
- Mixing the wood particles or fibers with resin, paraffin wax and other additives;
- Forming the panel,
- Consolidating and curing it under pressure and heat, and then
- Sanding and sawing to desired dimensions.
Environmental Details
Composite wood panels offer the following LEEDv4 credits:
Materials & Resources
Building Product Disclosure & Optimization – Sourcing of Raw Materials
Use products that meet at least one of the responsible extraction criteria for at least 25% by cost of the total value of permanently installed building products. (Recycled Content is one of the responsible extraction criteria)
Location Valuation Factor
Products that are extracted, manufactured and purchased within 100 miles of the project site are valued at 200% the product cost for meeting other Materials & Resources credits.
Materials & Resources
Building Product Disclosure & Optimization – Sourcing of Raw Materials
Use products that meet at least one of the responsible extraction criteria for at least 25% by cost of the total value of permanently installed building products. (FSC Certified wood products are one of the responsible extraction criteria).
Materials & Resources
Building Product Disclosure & Optimization
Material Ingredients
Use 20 products from 5 manufacturers that use various programs to demonstrate the chemical inventory of their product(s)
Materials & Resources
Building Product Disclosure & Optimization
Environmental Product Declarations
Use 20 products from 5 manufacturers that have LCA or EPD data as outlined by USGBC.
Indoor Environmental Quality
Low-emitting materials
100% of all composite wood products in the project must meet the CARB emissions compliance standards (CARB approved ULEF or NAF Exempt)
Further Resources
A white paper on the science-based LCA reports of wood composite panels showing they store more carbon than is released during their cradle-to-gate manufacturing processes: Life cycle assessment of Particleboard, Medium Density Fiberboard, and Hardboard /Engineered Wood Siding & Trim.
Particleboard and MDF Composite Wood Panel Suppliers
- ARAUCO
- Egger
- Great Plains MDF
- Kronospan
- Panolam
- Roseburg
- Tafisa
- Uniboard
- Weyerhaeuser MDF